CATUVAB® R&D
Outline of Research & Development Program
We are developing innovation for autologous blood transfusion in cancer patients using our medical device CATUVAB®.
Conducted Studies
Lindis Blood Care has conducted a series of preclinical and clinical studies to evaluate the efficacy and safety of CATUVAB® and ABCR-Technology.
These studies range from in vitro proof-of-principle investigations to multicenter confirmatory trials and collectively provide robust evidence supporting the clinical application of CATUVAB® for intraoperative blood processing.
Proof of Principle
2018
In vitro study: Blood spiked with tumor cells, treated with CATUVAB® and IBS device. Tumor cells and residual antibody measured in final erythrocyte concentrate.
Key Endpoints: Tumor cell removal residual antibody levels.
Key Findings: No residual tumor cells detected, low residual antibody levels.
Pilot Study
2019-2020
Ex vivo study: 15 patients with EpCAM-positive carcinomas, intraoperative blood treated with CATUVAB®. Tumor cells and antibodies measured.
Key Endpoints: Tumor cell removal (EpCAM+), safety parameters.
Key Findings: No residual EpCAM-positive tumor cells detected, safe procedure.
REMOVE Study
2021-2023
Multi-center confirmatory study: Up to 136 patients with EpCAM-positive carcinomas, intraoperative blood treated with CATUVAB®. Adds retransfusion of erythrocyte concentrates.
Key Endpoints: Tumor cell removal (EpCAM+), safety parameters, retransfusion feasibility.
Key findings: Designed to confirm safety and efficacy for CE certification.
With the REMOVE study, all study results demonstrate the efficacy and safety of CATUVAB®.
REMOVE Study (Study completed Q4/2023)
Multi center study (6 centers).
Study endpoints: tumor cell removal, cytokine
Levels, residual antibody assessment.
Data from – 136 Patients evaluated.
80 re-transfusions of Erythrocyte
Concentrates (EC)
Results:
- Efficacy Endpoint: Residual tumor cells in final EC after correctly performed procedure.
-
60 Pts with Tumor Cells in EC:
- 59 Pts: 0 Tumor Cells left
- 1 Pts: 4 Tumor Cells left
- Highest amount of Tumor Cells found in the reservoir of IBS: 4.2 million completely removed by CATUVAB®
-
Safety Endpoints: Residual antibody and Cytokine levels in final EC.
- Low ng amounts of residual antibody 10% of final EC, all others below LLOQ.
- Cytokines always reduced after CATUVAB®/MAT procedure.
CATUVAB® efficacy
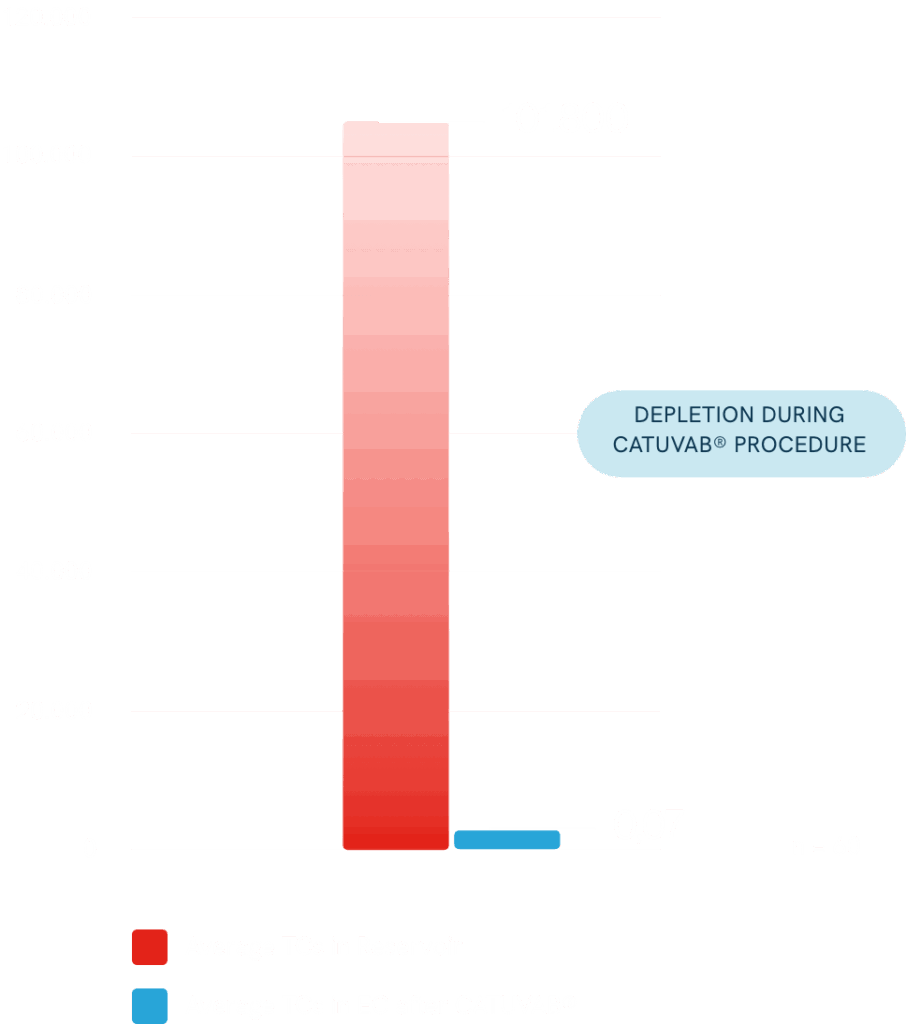
All efficacy and safety endpoints met with high statistical significance.
Pilot Study
Lindis Blood Care performed successfully an Exploratory Study, („Pilot Study“) at a German University. In this study the CATUVAB® procedure was used to treat intraoperative blood from 15 Patients during an oncological surgery. To demonstrate the efficacy of CATUVAB®, potentially remaining tumor cells as well as antibodies were assessed with very sensitive detection methods in the erythrocyte concentrates (EC), besides other safety parameters.
Based on convincing data from the PILOT STUDY published by Winter et al., BMC Anesthesiol, 2021, LBC`s Confirmatory Study REMOVE was started.
Ex vivo Pilot Study: CATUVAB® shown to be safe and effective
-
Timing:
Study completed in 2020.
-
Study design:
15 volunteers from surgeries of different EpCAM positive carcinomas, Parameters measured in the intraoperative blood and ECs:- EpCAM positive tumor cells
- Safety parameters
-
Summary:
- Study was successfully completed
- No residual EpCAM positive Tumor Cells were found after use of CATUVAB®.
In Vitro data
Lindis Blood Care has started the development of CATUVAB® by generating in vitro data regarding the ability of CATUVAB® to remove EpCAM positive tumor cells from blood, including cancer stem cells
Spiking Study Tumor Cells
Experiment | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
Reservoir | 95.000 | 169.000 | 44.000 |
Post CATUVAB® | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Residual Antibody

Proof of Principle demonstrated in an in vitro study
-
Timing:
Study completed in 2019.
-
Study design:
Blood drawn from volunteers was spiked with tumor cells, samples then treated with CATUVAB® and a standard IBS device Samples then screened for tumor cells and residual antibody in the final erythrocyte concentrate (EC) after leukocyte depletion filtration.
-
Results summary:
Also at a very low antibody concentration no residual tumor cells were detected in the final erythrocyte concentrate.